John Doe
General SurgeonPretium saepe pariatur ornare cillum repudiandae inceptos iaculis cumque vulputate sequi neque quos exercitation aliquip interdum, veniam? Aute error, elit!
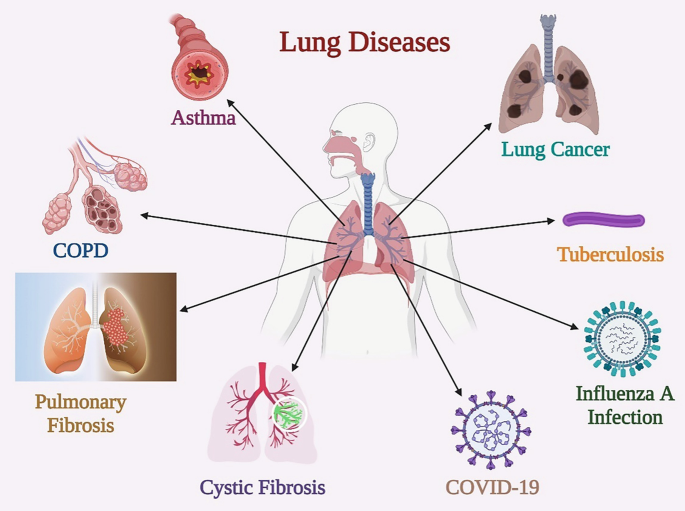
Overview
Lung diseases affect the airways, lung tissues, or blood vessels in the lungs. Conditions such as asthma cause airway inflammation, while COPD and TB can severely damage lung function, leading to chronic respiratory problems.
Causes
Lung diseases can be caused by smoking, exposure to harmful pollutants, allergens, or occupational hazards like asbestos. Infections, genetic predispositions, and long-term exposure to secondhand smoke can also lead to lung conditions.
Symptoms
Common symptoms include chronic cough, shortness of breath, wheezing, chest pain, and fatigue. In severe cases, lung diseases can result in respiratory failure, where oxygen levels drop dangerously low.
Treatment
Treatment depends on the specific condition and its severity. Options include medications like bronchodilators, steroids, or antibiotics for infections. In advanced cases, oxygen therapy or surgical interventions may be required.
Precautions
Preventive measures include avoiding smoking and exposure to pollutants, wearing protective masks in hazardous environments, and maintaining regular vaccinations for respiratory infections. A healthy lifestyle with regular check-ups can help monitor and manage lung health.